
USE CASES
Blockchain Solutions for Central Bank Digital Currency (CBDC)
Central Bank Digital Currency (CBDC) is a digital form of central bank money that offers central banks unique advantages at the retail and wholesale levels, including increased financial access for individual customers and a more efficient infrastructure for interbank settlements.
What Is Central Bank Digital Currency?
A Central Bank Digital Currency (CBDCs) is a digital form of central bank money, which is legal tender created and backed by a central bank that represents a claim against the central bank and not against a commercial bank or a Payment Service Provider (PSP). CBDC is managed on a digital ledger (which can be a blockchain or not), expediting and increasing the security of payments between banks, institutions, and individuals. According to a recent study conducted by the Bank for International Settlements, more than 70% of institutions are actively researching and developing proofs of concept for CBDCs. Here are three aspects that define a central bank digital currency:
Digital assets. CBDCs are digital assets. They are accounted for in a digital ledger (distributed or not) that acts as the single source of truth.
Central bank backed. CBDC represents claims against the central bank, just as banknotes do.
Central bank controlled. The supply of CBDC is fully controlled and determined by the central bank.

ON-DEMAND WEBINAR
CBDCs and Stablecoins
In this webinar with industry experts, you’ll learn the fundamentals of CBDC and the potential benefits, risks, and challenges for both central banks and global economic infrastructure.

FEATURED WHITE PAPER
Central Banks and the Future of Digital Money
An introduction to central bank digital currencies (CBDCs), their advantages for retail and wholesale payments, and a proposed architecture for a successful implementation on Ethereum.

“CBDCs give central banks future-oriented tools to allow them to implement monetary policy in more direct, innovative ways and keep pace with technological change.”
Joseph Lubin
Founder of Consensys and Co-Founder of Ethereum
What Are the Use Cases of CBDCs?
CBDC can be built for retail and/or wholesale payments. While a retail CBDC refers to a digital version of cash, a wholesale CBDC refers to a new infrastructure for interbank settlements. Central banks that have been trialing CBDC have been focusing especially on fast, low-cost payments.
Retail. Retail CBDC is used for payments between individuals and businesses or other individuals, akin to digital bank notes. The daily volume of retail CBDC is usually greater than 100,000,000 transactions.
Wholesale. Wholesale CBDC is used to facilitate interbank settlement, ie. payments between the few banks and other entities that have accounts at the central bank. The daily volume of wholesale CBDC is usually less than 100,000 transactions.
What Are the Benefits of CBDC?
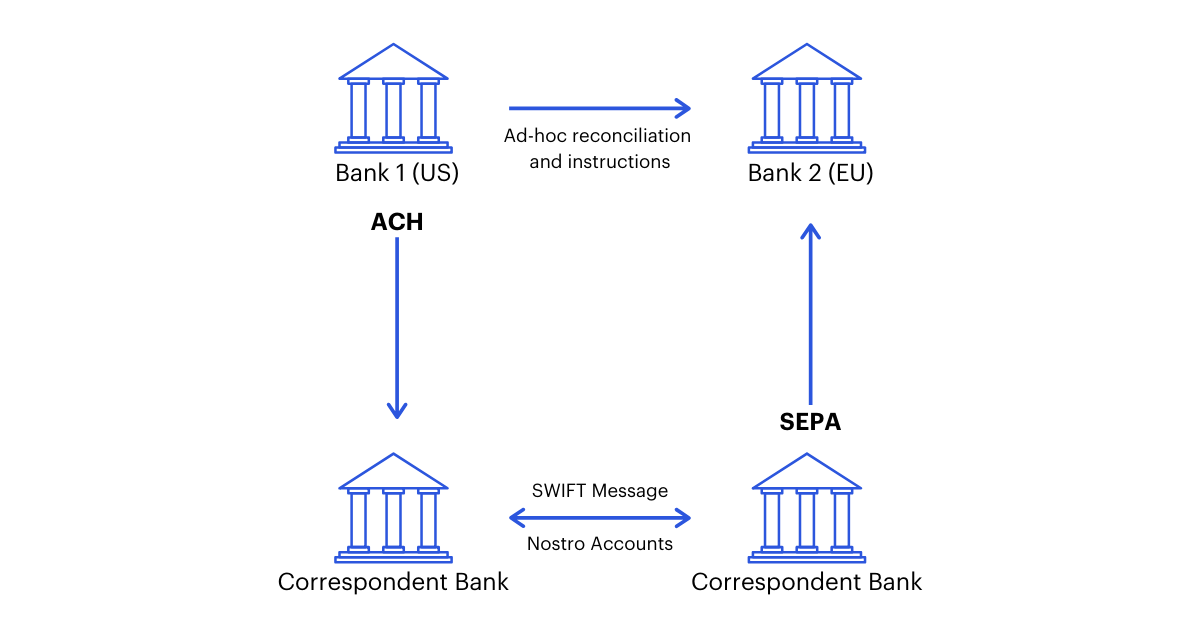
Central bank financial infrastructure currently faces a number of challenges, from costly payment settlement to the decreasing use of bank notes and lack of financial access for citizens far from bank branches. Studies have estimated that the cost of clearing and settling securities for central banks in G7 countries is over $50 billion per year, due in large part to the resources required to transfer assets and reconcile accounts. Moreover, today’s cross-border payment systems involve the transfer of assets and sensitive transaction data through several different correspondent banks, exposing institutions and individuals to settlement and operational risk.
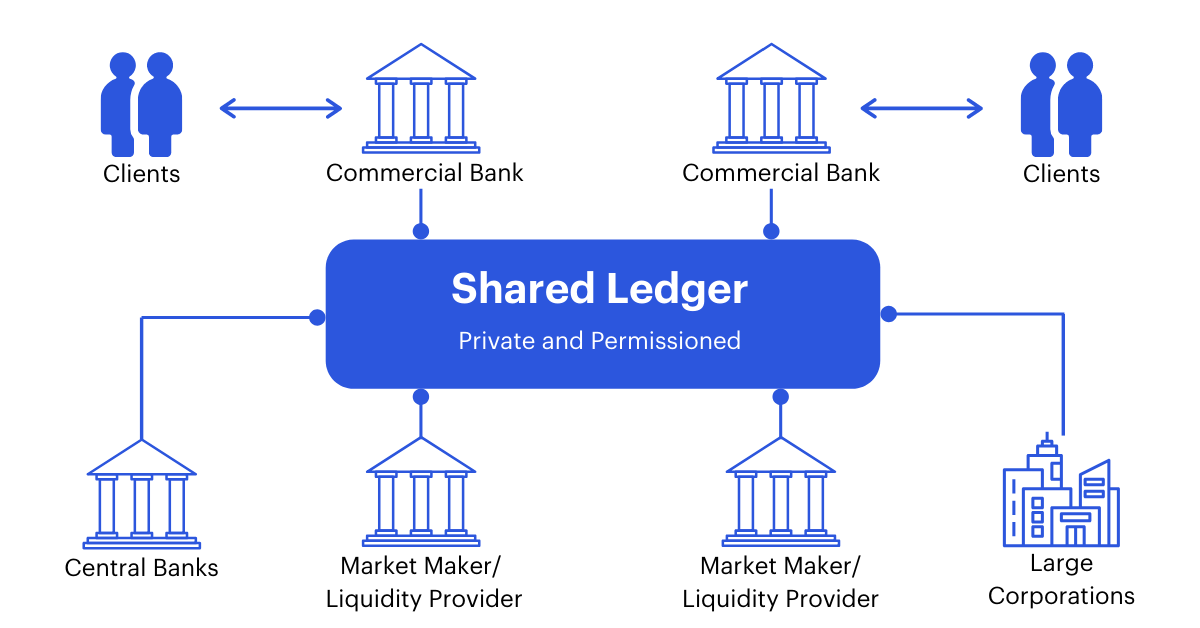
Blockchain-based CBDC solves for the inefficiencies and vulnerabilities in our current central banking infrastructure by simplifying the creation of a secure payments system that serves as a large-scale, decentralized clearing house and asset register.
Benefits of Retail CBDC
Increase availability. Digital currency can be distributed on mobile devices, increasing access and usability for citizens who are far from bank branches and cannot access physical cash.
Streamline reconciliation. A CBDC is natively digital and does not require the costly and time-consuming reconciliation currently needs for e-commerce and cross-border payments.
Foster digital innovation. CBDC’s platform-based software model lowers barriers to entry for new firms in the payments sector, fostering competition and innovation and pushing financial institutions toward the globalization of services.
Enhance monetary policy. CBDC gives central banks direct influence over the money supply, simplifying the distribution of government benefits to individuals and improving control over transactions for tax controls.
Benefits of Wholesale CBDC
Improve interbank payment settlement. Through automation and decentralized netting solutions, CBDC payments are settled instantly between counterparties on an individual order basis, reducing the risk of overnight batch processing and collateralization.
Reduced counterparty risk. CBDC mitigates credit risk in cross-border payment transactions by enabling payment-versus-payment settlement for transfers in different currencies.
Participate in digital asset markets. As more tokenized asset markets emerge, there will be a need for tokenized payments. CBDC provides a large-scale, decentralized clearing house and asset register to help foster the digital assets revolution.
Stay competitive. Even though the cost of real-time money transfers has been reduced by centralized platforms like SEPA in Europe, most financial institutions charge customers above cost. CBDC allows end users to benefit from streamlined banking infrastructure and ensures central banks maintain a role in interbank settlement amidst the wider adoption of stablecoin technology.
Why Blockchain and Ethereum for CBDC
Blockchain technology bring unique advantages to a CBDC. Ethereum in particular is the most production-ready blockchain to support CBDC requirements in terms of scalability and privacy.
System trust. A blockchain-based CBDC enables central banks to control the currency while protecting the privacy and independence of the CBDC’s use to the end users. We believe it is critical that users are not locked in by intermediaries so that they trust and use the CBDC.
Programmability. CBDC rules can be hard-coded in the protocol to facilitate compliance, i.e. wallet thresholds or third-party access to the system.
Data availability. Distributed systems such as blockchains ensure data availability and resilience, in addition to trust and transparency around transaction history. Ethereum has proven its capacity to support very large networks with 10k+ nodes and hundred thousands of users.
Innovation. A blockchain-based CBDC benefits from the innovative products and services that are being built across the open source blockchain ecosystem, including non-custodial wallets, zero-knowledge cryptography, and decentralized finance. Ethereum is the largest blockchain ecosystem in the world, with over 350,000 developers.
For a deeper dive on Ethereum’s unique advantages for enterprise blockchain solutions, read our Introduction to Enterprise Ethereum.
CBDC News and Insights


A CBDC FAQ addressing questions around payments, monetary and financial stability, CBDC functionalities, technology, infrastructure, and further innovations for Central Banks.


INSIGHT REPORT | A CBDC FAQ addressing questions around payments, monetary and financial stability, CBDC functionalities, technology, infrastructure, and further innovations for Central Banks.


Jean Michel Godeffroy, a monetary policy expert with sixteen years experience as director general at the European Central Bank, shares his insights on CBDCs


Wholesale vs. Retail? Delivery vs. Payment? We explore the design expectations and technical approaches of four recent Consensys CBDC pilots.


Key principles of retail CBDC and the state of central bank blockchain adoption around the world.


Why the risk of inaction is greater than the risk of innovation for the world’s largest financial institutions.


An intro to CBDCs, why they matter, and central banks that are actively exploring implementation.


The latest on central bank digital currencies, stablecoins, and all the blockchain highlights from the World Economic Forum's 2020 edition.


An article on the growing interest in CBDCs, featuring an interview with Consensys Managing Director Ken Timsit.